Gravity definition and facts for kids
The word “gravity” comes to us from Latin. It means “weight”, and this is how we call the force that gives weight to objects. This is such a physical force, due to which people are held on Earth’s surface, and the Earth itself takes its place in its orbit. Even though people already in ancient times wondered why all objects fall down, modern scientists still have questions about how gravitational force works. So what is it?
In simple terms, gravity is the kind of attraction that exists between any two material bodies. Everything that is made of matter that can be touched has its own gravity. These are any objects, even fruits and vegetables (pears, oranges, etc.), human bodies, and our planet itself.
Despite the term weightlessness, gravitational forces cannot be avoided. Astronauts in low-earth orbit also have gravity, but they move so fast that they never approach the center of the planet and are constantly in free fall.
There is a regularity that says that the degree of gravity of a body is proportional to its mass. The more mass an object has, the more gravitational force it has. Planet Earth is at the same time the largest and closest object to us, so all objects are attracted by its gravity. That is why fruits that have fallen from a tree will fall straight down to the ground and not be attracted to other people.
Distance between objects also affects gravitational attraction. The further objects are from each other, the less gravity between them. For example, in space, there is a point where the attraction of Mars becomes stronger than that of Earth.
Scientists have found that there are four fundamental forces in our world. These are gravity, electromagnetic force, weak interaction, and strong interaction. Forces change the motion of an object, and these four fundamental forces determine how everything in the universe interacts.
Gravity is the weakest force, but it can be seen in nature more than others, and on a large scale, it has the greatest impact on the entire world. Gravity is both the reason why humans are held on Earth’s surface and why planets are held in orbit around the Sun in their place and the solar system in the galaxy as a whole.
You may also be interested:
Earth facts for kids: amazing facts and lots of useful information to introduce your child to our beautiful planet 🌏
Gravity has a few different effects on our world, in addition to the fact that gravity not only holds things on the ground but also gives them weight. Items weigh less on planets that have less gravity. The gravity of the Earth’s natural satellite — the Moon — provides the sea’s ebb and flow on Earth. Gravity keeps the Earth moving in its orbit and preserves the atmosphere of our planet, allowing creatures to breathe, as well as protecting them from solar radiation.
Gravity is also a very important phenomenon in the creation of the universe. The gases that fill our universe are attracted to each other by gravity, forming clusters, stars, and planets, as well as other large objects. Some scientists believe that particles after the Big Bang formed a collapse in the universe, but it stopped precisely due to gravity. Gravity brings stellar systems closer together, so galaxies are formed, and this is fundamentally important for the entire universe.
What does gravity depend on?
This is a very interesting question.
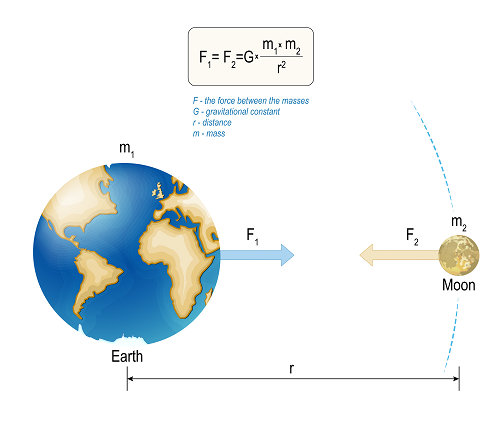
Based on the law of universal gravitation, the gravitational attraction between two material objects always depends on the mass of each of these objects, as well as on the distance between them.
This is how the formulation of the law of universal gravitation sounds:
There is an attractive force between any two material objects, which acts in a straight line, while the magnitude of this force is directly proportional to the mass of each of these bodies and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
In the form of a formula, the law of universal gravitation is written as follows:
F = G*M1*M2 / R2, where
F is the force of attraction between two bodies,
М1 and М2 are the masses of particles,
R is the distance between them,
G = 6.6742 · 10–11 m3 / (s2 · kg) is the gravitational constant.
Who discovered the force of gravity?
People in ancient Greece believed that gravity is inside the object itself, and this allows objects to be attracted to the Earth. Heavy people are naturally attracted to the Earth, while light tongues of a flame leap towards the sky. On the contrary, Indian scientists, particularly Aryabhata, said that some force holds objects on Earth. However, his theory places the Earth at the center of the universe.
Around 600 AD, one of the mathematicians named Brahmagupta first described gravity as a force of attraction. But even after that, people did not stop thinking about the nature of gravitational forces. This is how it was during the Renaissance.
Galileo is said to have thrown objects from the side of the falling Leaning Tower of Pisa to watch what happens when they fall. Regardless of whether the tower was used for such experiments, Galileo established that all material bodies accelerate at the same speed during a fall.
Other scientists also based their arguments on experiments. Grimaldi and Riccioli calculated the value of such a parameter, which was later called the “gravitational constant.” There is also another work on gravitational forces that describes Johannes Kepler’s astronomical theses. This scientist calculated the trajectories of the orbits of the known planets based on his theory. But nevertheless, in the modern world, it is generally accepted that the formulation of the classical law of universal gravitation was proposed by a scientist named Isaac Newton.
On the decline of his days, Isaac Newton told how it happened. He was walking in an apple garden at his parents’ estate and suddenly saw the Moon in the daytime sky. And right there, before his eyes, an apple came off the branch and fell to the ground. At that time, Newton was already working on his famous laws of motion. He already knew that, for example, an apple would fall vertically down towards the Earth under the influence of gravity. He also understood that the Moon is not just in the sky but revolves in its orbit around our planet. Respectively, a force acts on the Moon that does not allow it to deviate from its course and fly into space.
Then the thought came to him that most likely, it is the same force that makes the apple fall to the surface of the Earth and leaves the Moon in its place in space. Newton suggested that a number of events, seemingly having nothing in common, are caused by one reason — the forces of gravity. After doing a lot of work, this man came to the idea that two bodies are attracted to each other so that the force of gravity between them should be directly proportional to the mass of these bodies and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The importance of gravity in space and on Earth
Newton knew that gravity is the force that pulls objects towards each other. And his laws predicted the intensity of this force with amazing accuracy. But how exactly does gravity work? What is its fundamental importance? How is the Moon attracted to Earth hundreds of thousands of kilometers away?
But today, man has gone beyond the circle of aspects in which Newton’s theory was formed in the 17th century. In the early 20th century, Albert Einstein unveiled a new vision of how gravity can be viewed. He described this scientific theory in the “Theory of Relativity” created by him.
This theory explains the gravitational interactions of bodies on a cosmic scale by the curvature of space by gravitating bodies. The amount of curvature is proportional to the mass of the taken objects. But on the scale of the Earth’s surface and movements on it, there is no sense in using general relativity since it cannot give anything new, and if it does, then only scanty corrections in calculations can be completely neglected.
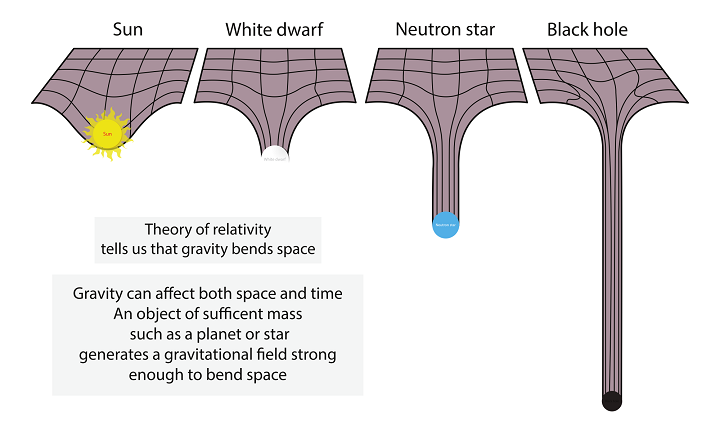
Nevertheless, this theory, created by Einstein, describing gravity as the curvature of space and time by massive bodies of space, helps scientists simulate the interaction of large objects in the universe. This explains many of the happenings of space. In simple terms, outer space is represented as one large canvas stretched along with the entire universe. Massive objects are located on this canvas, curving its surface. Thereby, nearby objects fall under the influence of this curvature. Thus, the bodies are attracted to each other.
And what can be said about gravity on our planet?
If gravity is a general concept that all objects in the universe have, then gravity on our planet is a special case of the manifestation of this concept. Our planet attracts all material objects. Thanks to this, people and all animals can freely move on land. Water bodies remain within their shores, and the air atmosphere is kept on the planet and does not fly into space.
You may also be interested in other “Physics for kids” topics :
- States of matter: solids, liquids and gases
- How does electricity work?
- Force and motion
- Magnets for kids: how does magnetism work?
What is weight?
Weight is the force with which any material body, due to the Earth’s attraction, affects support or suspension.
Weight and gravity are of different physical nature. The force of gravity arises from the interaction of the body and the Earth. Bodyweight arises from the interaction of the body and the support (suspension). In this case, the support (suspension) is deformed, which leads to the appearance of an elastic force. It follows from Newton’s third law that the weight of a body, that is, the force with which the body presses on the support (or stretches the suspension), coincides in magnitude with the force acting from the support on the given body. The force with which the support presses on the body is called the reaction force of the support.

Bodyweight should not be confused with body mass. The mass of a body is a scalar quantity, measured in kilograms. The weight of an object, that is, the weight of a material body, is a vector quantity, and we must measure it in units called Newtons.
Interesting facts about gravity
- For people who have been in space and returned to Earth, it is quite difficult at first to get used to the force of the gravitational effect of our planet. Sometimes it takes several weeks.
- Some studies show that in zero gravity, the human body can lose 1% of its bone marrow mass in a period of one month.
- Among the planets, Mars possesses the smallest gravity in the solar system, and Jupiter has the greatest.
- The bacteria known to mankind as Salmonella causes intestinal diseases. These bacteria behave more aggressively in a weightless state and can harm humans more severely.
- Of all the known astronomical objects in the universe, black holes have the greatest gravity. If we take a black hole the size of a tennis ball, it will have the same gravity as the planet Earth.
- In different places on our planet, the force of attraction will also be different. For example, in the Hudson Bay area in Canada, it will be lower than in other places on our planet.
- Gravity is not that strong. Some small magnet, clinging to the metal ceiling, overcomes it with ease.
- To overcome the gravity of the Earth, the rocket needs to accelerate to 11.2 kilometers per second.
- In the absence of gravity, the flame around a burning match or candle spreads in all directions and does not stretch upward.
- Without gravity, carbonated drinks can be life-threatening, as the gases they contain will not be properly distributed throughout the body.
- The Moon’s gravity is six times weaker than the Earth’s. Still, objects on the Moon’s surface fall faster since there is no atmospheric resistance.

new engaging articles